Introduction to Immersive Technologies and Their Growing Significance
Immersive technologies, encompassing Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed
Reality (MR), and Extended Reality (XR), are revolutionizing the way we interact with digital content by blending the physical and virtual worlds.
These technologies create experiences that engage multiple senses, making digital interactions more lifelike and engaging.

Understanding Immersive Technologies
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR immerses users in a fully digital environment, replacing the real world with a simulated one. By wearing VR headsets, users can explore and interact with 3D worlds, often used in gaming, training simulations, and virtual tours.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their environment. This is commonly experienced through smartphones or AR glasses, integrating virtual elements like images, sounds, or data with the physical world.
- Mixed Reality (MR): MR combines aspects of both VR and AR, allowing real and virtual elements to interact in real-time. For example, users can manipulate virtual objects that appear alongside physical ones, often requiring specialized hardware like
Defining Virtual Reality (VR)

What is Virtual Reality?
Virtual Reality (VR) is a cutting-edge technology that immerses users in a fully simulated, computer-generated environment, effectively transporting them to a different reality.
Unlike traditional interfaces that display content on a screen, VR places the user inside an interactive 3D world, engaging multiple senses to create a convincing experience.
This immersion is achieved through specialized hardware and software that work in tandem to simulate a user’s physical presence in a virtual environment.
How Does VR Work?
To create this immersive experience, VR relies on a combination of hardware and software components:
VR Hardware
- Headsets: These are the primary devices that display the virtual environment to the user. They encompass the user’s field of vision and often include built-in sensors to track head movements, ensuring that the virtual world adjusts in real-time as the user looks around. Examples include the Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR.
- Controllers: Handheld devices that allow users to interact with the virtual environment. They can simulate hands, tools, or other objects, enabling actions like grabbing, pointing, or shooting within the VR world.
Defining Augmented Reality (AR)
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information—such as images, videos, or data—onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their environment.
Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which immerses users in a completely virtual environment, AR integrates virtual elements into the physical world, allowing for an interactive experience that blends both realms.

How Does AR Work?
AR operates by superimposing digital content onto the user’s view of the real world, achieved through a combination of hardware and software components.
AR Devices
- Smartphones and Tablets: These devices utilize their cameras to capture the real world and display augmented content on their screens. Applications like Pokémon Go exemplify this, where virtual characters appear within the user’s real-world surroundings.
- AR Glasses: Wearable devices, such as Microsoft HoloLens and Google Glass, project digital information directly onto the user’s field of vision, allowing for hands-free interaction with augmented content.
AR Software
AR applications rely on advanced software to function effectively:
- Computer Vision: This technology enables devices to interpret and understand visual data from the real world, identifying objects and environments to accurately overlay digital content.
- Motion Tracking: Sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes detect the user’s movements, ensuring that the augmented content adjusts in real-time to maintain alignment with the physical world.
Applications of AR
AR technology has been adopted across various industries, offering innovative solutions and enhancing user experiences:
- Navigation: AR can overlay directional arrows and information onto live views of streets, assisting users in real-time navigation.
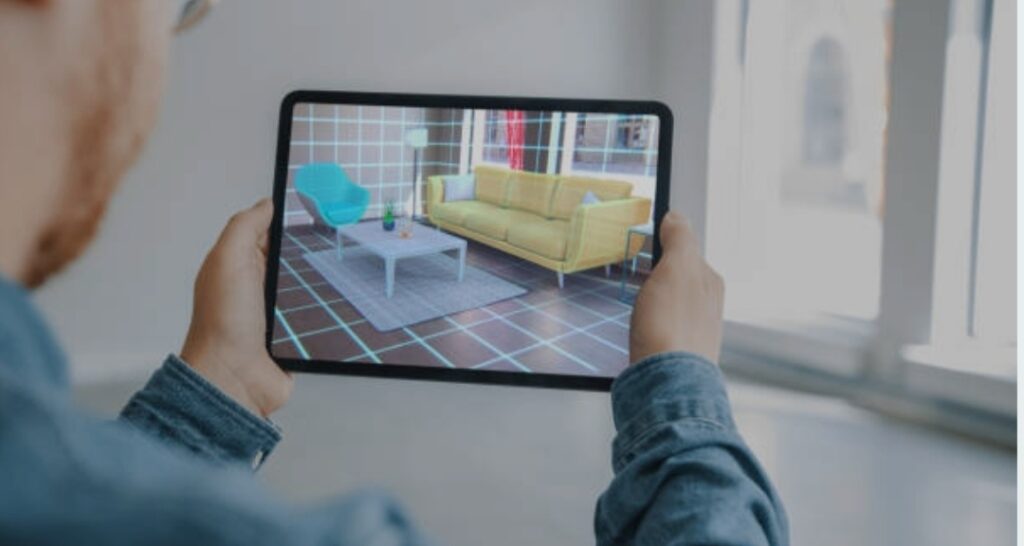
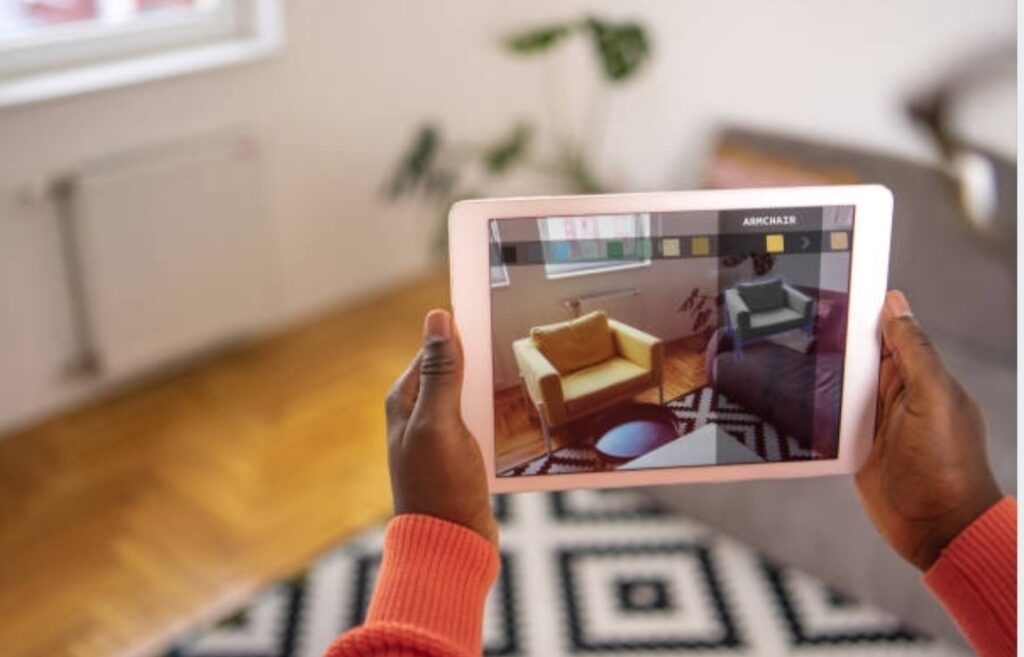
- Retail (Virtual Try-Ons): Retailers utilize AR to allow customers to visualize products, such as clothing or furniture, in their own space before making a purchase.
- Maintenance: Technicians can use AR to receive real-time information and guidance while performing repairs, improving efficiency and accuracy.
- Gaming: AR has revolutionized gaming by integrating virtual elements into the real world, creating immersive and interactive experiences.
Understanding these aspects of AR provides insight into how it differs from VR, highlighting the unique applications and experiences each technology offers.
Key Differences Between VR and AR
As technology continues to evolve, the debate surrounding VR vs AR differences has become increasingly relevant.
While both Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) offer immersive digital experiences, they operate in fundamentally different ways and cater to distinct use cases.
Below, we break down the key differences between VR and AR, helping you understand how each technology works and which might be better suited to your needs.

Level of Immersion – Full Virtual Experience vs. Real-World Enhancement
One of the most significant VR vs AR differences is the level of immersion they provide.
Virtual Reality (VR) – A Fully Immersive Experience
VR creates a completely digital environment where users are fully immersed in a computer-generated world.
This means that once you put on a VR headset, the real world disappears, and you are transported into a simulated reality that could be a game, a training simulation, or a virtual meeting room.
- VR replaces the real world entirely, making users feel as if they are physically inside the virtual space.
- This is achieved through head-mounted displays (HMDs) that cover the user’s entire field of vision, blocking out any real-world distractions.
- VR can simulate realistic sounds, haptic feedback, and even motion tracking, further enhancing the immersive effect.
- Popular VR experiences include gaming, military simulations, flight training, and virtual tourism.
Augmented Reality (AR) – Enhancing the Physical World
Unlike VR, Augmented Reality does not replace the real world. Instead, it enhances it by overlaying digital elements onto the physical environment.
This allows users to interact with digital objects while still being aware of their surroundings.
- AR keeps you connected to the real world while adding useful, interactive digital elements.
- The most common AR experiences are seen through smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses.
- AR applications are widely used in fields like navigation, retail, remote assistance, education, and entertainment.
A perfect example of AR in action is Google Maps’ Live View, which projects navigation arrows onto the real world when viewed through a smartphone camera.
Required Equipment – VR Headsets vs. AR-Enabled Devices
Another major distinction between Virtual Reality vs Augmented Reality is the type of equipment required for each experience.
VR Equipment – Headsets and Controllers
To experience VR, specialized hardware is required:
- VR Headsets: Devices like the Meta Quest 3, PlayStation VR2, and HTC Vive provide full VR experiences. These headsets contain high-resolution screens that create a 360-degree virtual world.
- Motion Controllers: VR users interact with the virtual world using motion-tracked controllers, which allow them to pick up objects, shoot weapons, or navigate through spaces.
- External Sensors (Optional): Some high-end VR systems require external sensors to track movement more accurately.
Since VR requires dedicated hardware, it is generally less accessible to the average user compared to AR.
AR Equipment – Smartphones, Tablets, and AR Glasses
Unlike VR, AR does not require an expensive headset. Instead, it works on everyday devices such as:
- Smartphones and Tablets: The vast majority of AR applications run on Android and iOS devices, using cameras and sensors to overlay digital objects onto real-world environments.
- AR Glasses and Headsets: Devices like Microsoft HoloLens, Magic Leap, and Apple Vision Pro provide a more immersive AR experience by displaying holograms directly in the user’s field of view.
Because AR technology can be accessed through common mobile devices, it has a much lower barrier to entry compared to VR.

User Interaction – Virtual Environments vs. Real-World Digital Overlays
Another VR vs AR difference lies in how users interact with digital content.
VR – Interacting Within a Fully Digital Environment
Since VR creates a completely virtual world, users interact with digital environments as if they were physically inside them.
For example:
- In a VR game, you might use a controller to pick up objects, move through the environment, or even swing a sword.
- In a VR training simulation, you can practice complex procedures like surgery or piloting an aircraft in a risk-free digital space.
AR – Blending Digital Objects with the Real World
AR users, on the other hand, interact with digital objects while remaining in the real world.
For example:
- Retail AR applications allow customers to try on clothes, shoes, or makeup virtually before purchasing.
- AR filters on social media (such as Snapchat and Instagram filters) let users add digital effects to their real-world faces.
- Industrial AR applications provide real-time guidance to technicians by displaying instructions on their AR glasses as they repair machinery.
Because AR supplements the real world rather than replacing it, it allows for a more natural and seamless interaction between physical and digital elements.
Accessibility – Widespread Use of AR vs. Specialized VR Equipment
The accessibility of each technology is another important consideration when comparing VR vs AR differences.
VR – More Expensive and Less Accessible
Virtual Reality experiences require specialized headsets, controllers, and sometimes high-performance computers or gaming consoles.
This makes VR:
- More expensive, as high-end VR headsets can cost several hundred dollars.
- Less accessible, since not everyone owns a VR headset.
- Limited to specific environments, as users need enough physical space to move around safely in VR.
AR – Easily Accessible on Everyday Devices
Augmented Reality, on the other hand, is much more accessible since it runs on common devices like smartphones and tablets.
This makes AR:
- Widely available, as nearly everyone owns a smartphone capable of running AR applications.
- More affordable, since AR does not require expensive hardware.
- Easier to use in public settings, as AR applications can be accessed discreetly without wearing bulky headsets.
Because of its accessibility, AR has seen widespread adoption in industries like retail, healthcare, and education, while VR remains more niche.
Which Technology is Right for You?
Both Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality offer exciting possibilities, but they serve different purposes depending on your needs.
- If you want full immersion and a complete escape into a digital world, VR is the better choice.
- If you prefer to stay connected to reality while enhancing it with digital elements, AR is the more practical option.
No matter which technology you choose, both VR and AR are shaping the future of digital interaction, gaming, and entertainment.
👉 Interested in trying out the latest VR or AR gear? Check out our list of the best VR headsets and AR glasses to find the perfect device for you!
Similarities Between VR and AR
While VR (Virtual Reality) and AR (Augmented Reality) have significant differences, they also share several core similarities.
Both technologies are built on advanced digital innovations and aim to create immersive and interactive user experiences that blend the real and virtual worlds in unique ways.
Let’s take a deep dive into the key similarities between VR and AR and explore how they function on similar technological principles while serving different purposes.

Technological Foundations – Shared Core Technologies Powering VR and AR
Both Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality rely on cutting-edge digital advancements to deliver their experiences.
Even though the execution varies, they share common technological foundations that enable them to create interactive, engaging, and immersive digital environments.
3D Modeling – The Backbone of Virtual and Augmented Experiences
One of the most fundamental similarities between VR and AR is the use of 3D modeling to create realistic objects and environments.
- In VR, entire virtual worlds are built using 3D computer-generated graphics, allowing users to navigate and interact with a fully digital space.
- In AR, 3D objects are overlaid onto the real world, blending digital elements with physical surroundings.
- Both technologies require high-quality 3D assets to ensure a realistic and engaging experience for users.
- Industries like gaming, architecture, retail, and education leverage 3D modeling to create interactive applications for both VR and AR.
For example, AR furniture apps like IKEA Place allow users to place 3D models of furniture in their homes using their smartphone cameras, while VR games like Half-Life: Alyx create fully immersive digital worlds through 3D graphics.
Real-Time Rendering – Bringing Digital Worlds to Life
Both VR and AR depend on real-time rendering to generate seamless, fluid, and interactive environments.
- Real-time rendering ensures that graphics respond instantly to user movements and interactions.
- VR games and simulations require high-speed rendering to prevent motion sickness and create a believable virtual world.
- AR applications need real-time tracking and rendering to align digital objects accurately with the user’s environment.
For example, Snapchat AR filters rely on real-time face tracking to apply filters dynamically as a user moves, while VR fitness games adjust gameplay in real-time based on the player’s movement.
Motion Tracking and Sensors – Enabling Immersive Interaction
Both technologies utilize motion tracking to enhance interactivity and realism.
- VR headsets use motion sensors like gyroscopes and accelerometers to track head movement, ensuring that the virtual world adjusts accordingly.
- AR relies on spatial tracking through smartphone cameras, LiDAR sensors, and GPS to place virtual objects in the correct real-world location.
- Some high-end AR and VR systems incorporate eye tracking and hand tracking for even more immersive experiences.
For instance, devices like the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3 use advanced tracking technology to allow gesture-based interactions in both VR and AR environments.

Purpose – Enhancing User Experiences with Immersive Environments
At their core, VR and AR exist to enhance user experiences by integrating digital elements into our interactions, entertainment, and work.
Although their methods differ, their ultimate goal is the same: to create engaging and immersive experiences that blend the digital and physical worlds.
Immersive Entertainment – Revolutionizing Gaming, Movies, and Social Media
Both VR and AR have revolutionized the way we experience entertainment.
- VR gaming offers complete immersion, allowing players to step inside a game world rather than simply watching it on a screen.
- AR gaming enhances real-world environments with interactive elements, as seen in games like Pokémon GO and Minecraft Earth.
- Virtual concerts and live events leverage both AR and VR to bring audiences closer to performers, even in remote locations.
- Social media platforms integrate AR filters and virtual spaces to create more engaging content for users.
For example, Meta’s Horizon Worlds (VR) lets users explore social virtual spaces, while Instagram and TikTok AR effects enhance videos with interactive graphics.
Training and Education – A Safer, More Engaging Learning Experience
Both VR and AR have become essential tools in education and professional training by offering realistic, interactive learning environments.
- VR training simulations allow medical students to practice surgeries in a risk-free virtual environment.
- AR applications in education help students visualize complex subjects like biology, history, and engineering by overlaying 3D models onto textbooks.
- Industrial training programs use VR-based simulations for hazardous work environments, such as firefighter and pilot training.
For example, NASA uses VR simulations to train astronauts before space missions, while AR anatomy apps help medical students understand the human body in an interactive way.
Business and Retail – Transforming Shopping and Work Environments
The business world has embraced both VR and AR to enhance customer experiences, improve productivity, and streamline operations.
- AR in eCommerce allows shoppers to try on clothes, glasses, or makeup virtually before making a purchase.
- VR in business meetings enables employees to collaborate in virtual workspaces regardless of location.
- Real estate agents use VR tours to showcase properties remotely, while AR home design apps help customers visualize renovations before construction.
For instance, companies like Nike and Sephora use AR-powered apps for virtual try-ons, while platforms like Spatial and VRChat offer virtual meeting spaces for businesses and social interactions.
The Common Ground Between VR and AR
While the debate over VR vs AR differences continues, it’s important to recognize that both technologies share strong similarities in their technological foundations and purpose.
- Both VR and AR rely on 3D modeling, real-time rendering, and motion tracking to create immersive digital experiences.
- Both are designed to enhance user interactions across entertainment, education, business, and training.
- As technology advances, the line between Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality is becoming increasingly blurred, with the emergence of Mixed Reality (MR) and Extended Reality (XR).
🚀 Are you ready to explore the world of VR and AR? Check out our list of the best VR headsets and AR devices to find the perfect tech for your needs!
Extended Reality (XR): The Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the Spectrum of Immersive Technologies
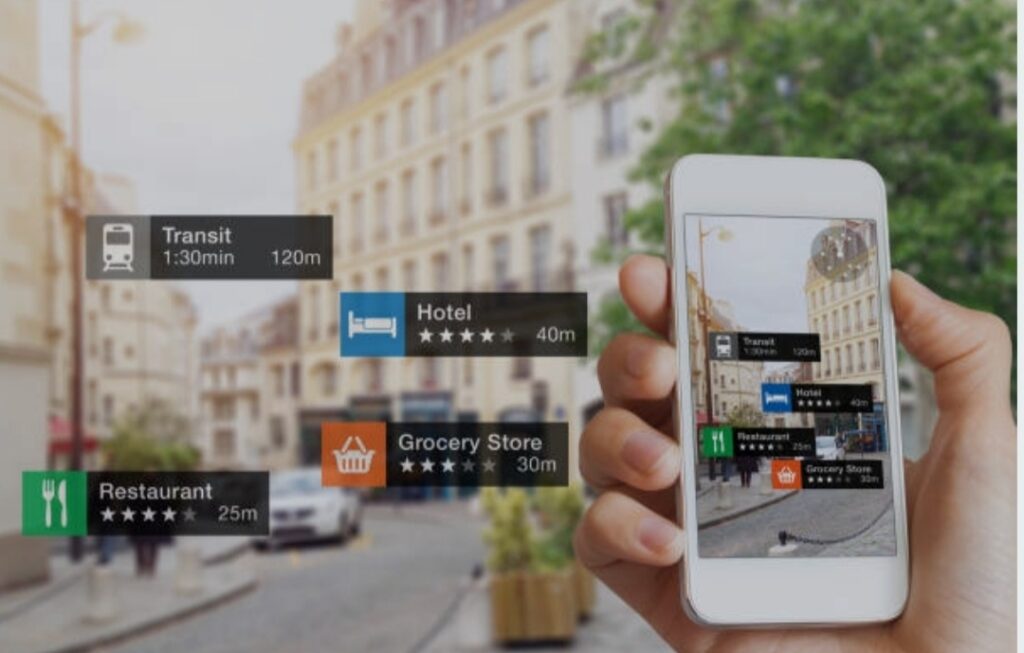
What is Extended Reality (XR)?
Defining XR and Its Components
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses a spectrum of immersive technologies, including Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed Reality (MR).
These technologies blend the physical and digital worlds to varying degrees, offering users enriched experiences that transcend traditional interfaces.
Components of XR: VR, AR, and MR
Exploring the Building Blocks of Extended Reality
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR immerses users in a fully simulated environment, completely replacing the real world with a digital one. This is typically achieved through headsets that provide 360-degree visuals and spatial audio, creating a sense of presence in a virtual space.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR overlays digital elements onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their environment. This is commonly experienced through smartphones or AR glasses, where digital information is superimposed onto the physical world.
- Mixed Reality (MR): MR combines aspects of both VR and AR, allowing digital and physical elements to coexist and interact in real-time. This creates a hybrid environment where users can interact with both real and virtual objects.
Mixed Reality (MR): Blending Physical and Digital Worlds
Understanding the Fusion of Real and Virtual Environments
Defining Mixed Reality
What Sets MR Apart in the XR Spectrum
Mixed Reality (MR) is a technology that merges the physical and digital worlds, enabling real-time interaction between the user, the environment, and virtual elements.
Unlike VR, which immerses users in a completely virtual environment, or AR, which overlays digital information onto the real world, MR allows for a seamless integration where physical and virtual objects coexist and can interact with each other.
Applications of Mixed Reality
How MR is Transforming Various Industries
- Education: MR offers interactive learning experiences, such as virtual dissections in biology classes or historical recreations in history lessons, enhancing student engagement and understanding.
- Healthcare: Medical professionals utilize MR for surgical simulations, patient anatomy visualization, and remote consultations, improving training and patient outcomes.
- Manufacturing: MR assists in product design, assembly line management, and maintenance procedures by overlaying digital instructions onto physical equipment, increasing efficiency and reducing errors.
- Entertainment: The gaming and film industries leverage MR to create immersive experiences where users can interact with digital characters and objects within their physical space.
Devices Enabling Mixed Reality
Technologies Powering MR Experiences
- Head-Mounted Displays (HMDs): Devices like the Microsoft HoloLens and Magic Leap One are equipped with sensors and cameras that map the physical environment, allowing digital content to interact seamlessly with the real world.
- Mobile Devices: Modern smartphones and tablets, equipped with advanced processors and cameras, can deliver MR experiences through applications that overlay digital elements onto the user’s surroundings.

VR vs AR Differences in the Context of XR
Comparing Virtual and Augmented Reality Within the Extended Reality Spectrum
Immersion Level
Degree of User Engagement in Virtual vs Augmented Reality
- VR: Provides a fully immersive experience, isolating users from the real world and placing them in a completely virtual environment.
- AR: Offers a partial immersion by overlaying digital elements onto the real world, allowing users to interact with both simultaneously.
Interaction with the Real World
How VR and AR Engage with Physical Environments
- VR: Users have no direct interaction with the physical environment while immersed in VR; all interactions occur within the virtual space.
- AR: Users interact with digital content that is superimposed onto their real-world environment, blending physical and virtual interactions.
Required Hardware
Devices Needed for VR and AR Experiences
- VR: Typically requires headsets with built-in displays, sensors, and controllers to navigate the virtual environment.
- AR: Often utilizes smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses that overlay digital content onto the real world through the device’s camera.
The Future of Extended Reality
Anticipating Developments in XR Technologies
Technological Advancements
Innovations Driving XR Forward
Advancements in processing power, artificial intelligence, and sensor technology are making XR devices more powerful and accessible.
These improvements are leading to more realistic and responsive XR experiences.
Broader Adoption Across Sectors
XR’s Expanding Influence Beyond Entertainment
Beyond gaming and entertainment, XR is making significant inroads into sectors like education, healthcare, retail, and remote collaboration, offering innovative solutions to traditional challenges.
Challenges and Considerations
Addressing the Hurdles in XR Adoption
- Technical Limitations: Issues like latency, limited field of view, and battery life need ongoing improvement to enhance user experience.
- Ethical and Privacy Concerns: As XR devices collect vast amounts of data, addressing privacy and ethical considerations is crucial to protect users.
Embracing the XR Revolution
Extended Reality (XR) represents a transformative shift in how we interact with digital content, breaking down the barriers between the physical and virtual worlds.
By understanding the distinct roles of VR, AR, and MR within the XR spectrum, we can better appreciate the unique experiences each offers and anticipate the innovative applications that lie ahead.
Explore the World of XR Today!
Dive into the immersive experiences offered by XR technologies and discover how they can revolutionize your personal and professional life.
Stay informed about the latest developments in VR, AR, and MR, and consider integrating these cutting-edge tools into your daily routines.
Industry Applications and Case Studies
Extended Reality (XR), encompassing Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Mixed
Reality (MR), has revolutionized various industries by introducing immersive technologies that enhance user experiences and operational efficiencies.
The distinctions between VR and AR are pivotal in understanding their unique applications across sectors.
VR immerses users in a completely virtual environment, while AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing real-world experiences.
This section delves into the profound impact of VR and AR in healthcare, education, entertainment, and retail, highlighting the differences between VR and AR applications in each domain.
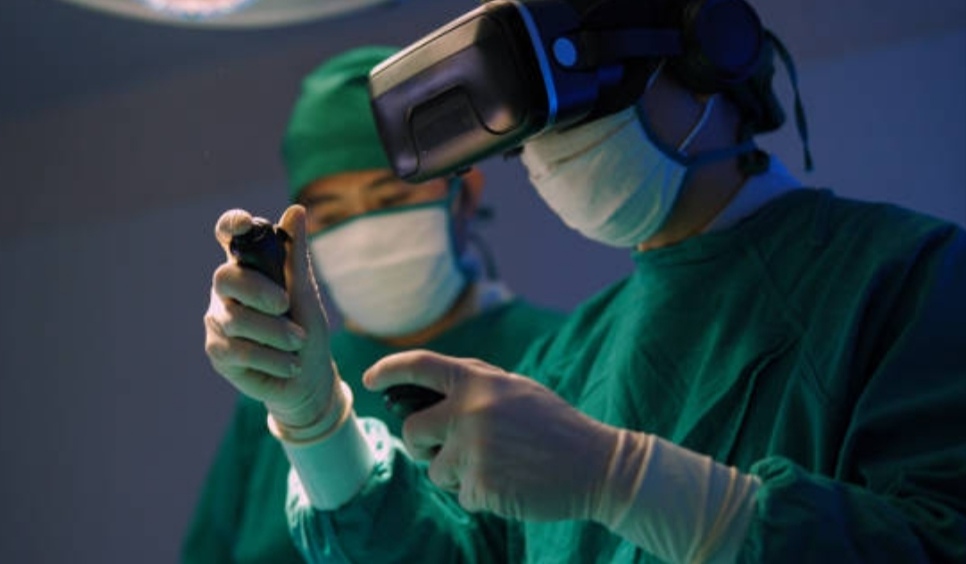
Healthcare
VR for Surgical Simulations
Virtual Reality has become a transformative tool in medical training and surgical preparation.
By creating immersive, computer-generated environments, VR allows surgeons and medical students to practice procedures in a risk-free setting.
These simulations provide realistic scenarios that enhance surgical skills, improve hand-eye coordination, and build confidence before actual operations.
For instance, VR platforms enable practitioners to rehearse complex surgeries, leading to reduced errors and improved patient outcomes.
AR for Vein Visualization
Augmented Reality has significantly improved patient care by assisting healthcare professionals in visualizing veins during procedures like intravenous insertions.
AR devices project images of a patient’s vascular structure onto their skin, making it easier to locate veins, especially in patients with difficult access.
This technology reduces the need for multiple insertion attempts, decreases patient discomfort, and enhances the efficiency of medical procedures.
By overlaying digital information onto the physical body, AR enhances the practitioner’s ability to perform tasks with greater accuracy.
Education
VR for Virtual Field Trips
Virtual Reality has opened new horizons in education by enabling virtual field trips, allowing students to explore historical sites, distant planets, or underwater ecosystems without leaving the classroom.
These immersive experiences provide interactive learning opportunities, making education more engaging and accessible.
For example, students can virtually visit ancient civilizations, enhancing their understanding of history and culture.
This application of VR not only enriches the curriculum but also caters to diverse learning styles.
AR for Interactive Textbooks
Augmented Reality has transformed traditional textbooks into interactive learning tools.
By scanning textbook images with AR-enabled devices, students can access 3D models, videos, and animations that elucidate complex concepts.
This interactive approach caters to visual and kinesthetic learners, making education more dynamic.
For instance, in biology classes, AR can bring molecular structures to life, allowing students to interact with and manipulate them for a deeper understanding.
This fusion of digital content with physical textbooks bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.

Entertainment
VR Gaming Experiences
Virtual Reality has revolutionized the gaming industry by offering immersive experiences that transport players into the game’s universe.
With VR headsets and motion controllers, gamers can interact with virtual environments in a lifelike manner, enhancing engagement and realism.
Games like “Beat Saber” and “Half-Life: Alyx” have set new standards for interactive entertainment, providing experiences that are both physically and mentally stimulating.
This level of immersion has redefined user expectations and continues to drive innovation in game development.
AR in Live Events for Enhanced Engagement
Augmented Reality has enhanced live events by providing interactive experiences that engage audiences in real-time.
Concerts, sports events, and exhibitions have integrated AR to display real-time statistics, interactive advertisements, and immersive storytelling elements.
For example, during live sports broadcasts, AR can overlay player statistics and game analytics onto the screen, enriching the viewing experience.
This technology bridges the gap between the physical event and digital content, offering audiences a more engaging and informative experience.
Retail
VR for Virtual Stores
Virtual Reality has transformed the retail landscape by enabling virtual stores where customers can browse and purchase products from the comfort of their homes.
These VR environments replicate the in-store experience, allowing shoppers to interact with products in a 3D space.
For instance, virtual showrooms enable customers to explore products as they would in a physical store, enhancing convenience and personalization.
This application of VR addresses the limitations of online shopping by providing a more immersive and interactive experience.
AR for Product Visualization in Real-World Settings
Augmented Reality has empowered consumers to visualize products in their real-world environments before making a purchase.
By using AR applications, shoppers can see how furniture fits in their living rooms or how a new appliance looks in their kitchen.
This technology enhances decision-making by providing a realistic representation of products in the intended setting.
For example, IKEA’s AR app allows customers to place virtual furniture in their homes, ensuring compatibility with existing decor.
This application of AR reduces uncertainty and increases customer satisfaction.
In conclusion, the integration of VR and AR across various industries has led to innovative applications that enhance user experiences and operational efficiencies.
Understanding the differences between VR and AR is crucial for leveraging their unique capabilities in specific contexts.
As these technologies continue to evolve, their impact on sectors like healthcare, education, entertainment, and retail is expected to grow, offering new possibilities for engagement and interaction.
Future Trends in VR and AR

Technological Advancements in VR and AR
Evolution of Hardware: Lighter Headsets and AR Glasses
The progression of VR and AR hardware is marked by a continuous drive toward enhanced user comfort and accessibility.
Manufacturers are focusing on developing lighter, more ergonomic headsets and sleeker AR glasses to facilitate prolonged use without discomfort.
For instance, the Meta Quest 3S, priced at $299, is set to launch on October 15, offering a more affordable and comfortable VR experience.
Additionally, Meta’s Ray-Ban augmented reality glasses have seen unexpected success, indicating a positive reception for wearable AR technology.
Enhancements in Display and Sensor Technologies
Advancements in display resolutions and sensor technologies are pivotal in delivering immersive experiences.
High-resolution displays reduce the screen-door effect, enhancing visual realism, while improved sensors enable precise tracking of movements and gestures.
These technological strides contribute to more seamless and engaging VR and AR interactions.
Market Growth: Projections and Emerging Markets
Global Market Expansion
The VR and AR markets are on a trajectory of significant growth. According to Fortune Business Insights, the global virtual reality market size was valued at $12.86 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow from $16.32 billion in 2024 to $123.06 billion by 2032.
This substantial increase underscores the escalating adoption of immersive technologies across various sectors.
Regional Adoption and Investment
North America has been a frontrunner in AR and VR investments, with a forecasted rapid growth in the next five years.
This trend is indicative of a broader global acceptance and integration of these technologies, with emerging markets recognizing the potential of VR and AR in enhancing business processes and consumer experiences.
Integration with AI: Enhancing VR and AR Experiences
AI-Driven Personalization
Artificial Intelligence is playing a crucial role in refining VR and AR experiences.
By analyzing user behavior and preferences, AI enables personalized content delivery, making interactions more relevant and engaging.
In the retail sector, AI-enhanced AR applications allow customers to virtually try on clothing and accessories, tailoring the shopping experience to individual tastes.
Improved Interaction and Realism
The synergy between AI and immersive technologies leads to more natural and intuitive user interfaces. AI algorithms facilitate realistic simulations and responsive virtual environments, enhancing the sense of presence in VR and AR applications.
This integration is pivotal in sectors like healthcare, where AI-powered VR can simulate complex surgical procedures for training purposes.

VR vs AR Differences: Understanding the Distinctions
Immersion Levels
Virtual Reality offers a fully immersive experience, transporting users into a completely digital environment.
In contrast, Augmented Reality overlays digital elements onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception without replacing their surroundings.
Hardware Requirements
VR typically requires headsets that encompass the user’s field of vision, creating an all-encompassing experience.
AR, however, often utilizes devices like smartphones or AR glasses, allowing users to remain aware of and interact with their real-world environment.
As VR and AR technologies continue to evolve, staying informed about the latest trends and advancements is essential.
Embracing these innovations can unlock new opportunities for businesses and individuals alike.
Explore the possibilities of VR and AR today to stay ahead in this rapidly changing landscape.
In conclusion, the future of VR and AR is characterized by rapid technological advancements, significant market growth, and deeper integration with AI.
Understanding the differences between VR and AR is crucial for leveraging their unique potentials.
As these technologies become more accessible and sophisticated, they are set to revolutionize various aspects of our lives, from entertainment and education to healthcare and beyond.
Challenges Facing VR and AR Adoption
Despite the rapid advancements in Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), several obstacles hinder widespread adoption.
While both technologies have made significant strides, there are technical, user experience, and security concerns that must be addressed before they become mainstream.
Understanding these challenges is crucial for businesses, developers, and users looking to integrate VR and AR into their daily lives.

Technical Limitations in VR and AR
Latency Issues and Performance Constraints
One of the biggest technical challenges in both VR and AR is latency, which refers to the delay between a user’s action and the system’s response.
For a truly immersive experience, this delay needs to be less than 20 milliseconds; otherwise, users can experience a disconnect between their actions and the virtual world.
In VR, high latency results in laggy movements, breaking immersion and making virtual environments feel unnatural.
In AR, where digital elements are overlaid onto real-world settings, even slight latency can cause misalignment, leading to poor user experience.
Possible Solutions:
- 5G Networks: With faster speeds and lower latency, 5G can significantly improve real-time rendering in both VR and AR applications.
- Edge Computing: By processing data closer to the user rather than in distant cloud servers, edge computing reduces latency.
- Optimized Graphics Rendering: Developers are working on rendering techniques that improve real-time visuals without overloading processing units.
Field of View and Display Limitations
Another major issue with VR and AR devices is their limited field of view (FoV).
Humans naturally have a horizontal field of view of about 200-220 degrees, yet most VR headsets currently offer around 100-120 degrees.
This restriction makes digital environments feel less immersive, forcing users to turn their heads unnaturally to take in their surroundings.
For AR devices, the issue is even more noticeable.
Many AR headsets, such as the Microsoft HoloLens 2, only offer a 52-degree field of view, making it difficult to overlay digital elements seamlessly onto real-world objects.
Possible Solutions:
- Advancements in Lens Technology: Companies like Meta and Apple are working on pancake lenses and micro-OLED displays to expand the field of view.
- Higher Refresh Rates: Increasing refresh rates to 90Hz or more can create smoother and more natural visuals.
- Dynamic FoV Adjustments: AI-driven solutions that dynamically adjust the field of view based on user focus.
Battery Life and Power Consumption
Both VR headsets and AR smart glasses require significant processing power, which drains battery life quickly.
Many standalone VR headsets, such as the Meta Quest 2 or HTC Vive Focus, last only 2-3 hours on a single charge.
Similarly, AR glasses like the Ray-Ban Meta Smart Glasses face limitations in terms of how long they can function without recharging.
Possible Solutions:
- More Efficient Chipsets: Companies like Qualcomm are designing processors specifically for VR and AR, reducing power consumption.
- Wireless Charging Integration: Future devices may include wireless charging capabilities for uninterrupted usage.
- Battery Innovations: Advances in solid-state batteries could significantly extend device usage times.
User Experience Challenges in VR and AR
Motion Sickness and Disorientation
One of the biggest barriers to VR adoption is motion sickness, also known as cybersickness.
This occurs when the visual input from the headset does not match what the inner ear perceives, leading to nausea, dizziness, and discomfort.
AR users may also experience eye strain from prolonged use of digital overlays, especially in bright outdoor environments where screens are difficult to read.
Possible Solutions:
- Higher Frame Rates: Keeping frame rates at 90 FPS or above helps reduce nausea.
- Adaptive Refresh Rates: Some VR headsets now use foveated rendering, where only the part of the screen being looked at is fully rendered.
- Improved Motion Tracking: More accurate sensors can better align physical movements with visual feedback, reducing motion sickness.
Comfort and Wearability Issues
Many VR headsets and AR smart glasses are bulky and uncomfortable, making prolonged use challenging.
Even lightweight VR headsets still put pressure on the nose and forehead, leading to discomfort after extended wear.
For AR glasses, the issue is even greater—most designs are still too heavy for all-day use.
Additionally, prescription lens compatibility remains a problem for many users.
Possible Solutions:
- Lightweight Materials: Companies are exploring carbon fiber and lightweight plastics to reduce weight.
- Modular Designs: Future devices may have interchangeable parts for personalized comfort.
- Custom Fit Options: More manufacturers are offering adjustable straps and customizable padding for different head shapes.

Privacy and Security Concerns
Data Collection and User Privacy
Both VR and AR devices collect vast amounts of personal data, including eye movements, hand gestures, voice inputs, and even facial expressions.
This raises serious concerns about how companies handle sensitive biometric data.
Many users worry that corporations could sell their data to third parties, leading to privacy breaches.
Additionally, AR applications that use cameras to scan surroundings could unintentionally capture sensitive personal information.
Possible Solutions:
- Stronger Data Encryption: Ensuring that all user data is encrypted before being transmitted.
- Clear Privacy Policies: Companies must be transparent about how user data is collected and stored.
- User Consent Controls: Giving users the option to opt out of certain data collection practices.
Cybersecurity Threats in VR and AR
With AR and VR headsets becoming more connected to the internet, they are vulnerable to hacking and cyberattacks.
For instance, hackers could manipulate virtual environments in VR training simulations, leading to misinformation or safety hazards.
Similarly, AR applications that rely on GPS and location tracking could be exploited for stalking or unauthorized surveillance.
Possible Solutions:
- Stronger Authentication Protocols: Using biometric authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Updates: Ensuring VR and AR software receives frequent patches to fix vulnerabilities.
- AI-Powered Threat Detection: Implementing AI-driven security measures to detect anomalies in real-time.
Overcoming VR and AR Adoption Barriers
Despite these challenges, the future of VR and AR remains promising.
As hardware improves, user comfort increases, and security measures strengthen, adoption rates will continue to rise.
Businesses and developers must address these challenges proactively to unlock the full potential of immersive technologies.
🔹 Are you ready to explore the next generation of immersive experiences?
🔹 Stay ahead of the curve—Check out the latest VR and AR devices here!
By solving these technical, user experience, and security issues, VR and AR can transition from niche technologies to mainstream innovations that revolutionize how we work, learn, and interact with the world.
Choosing Between VR and AR
Deciding between Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) depends on various factors, including intended use, budget, accessibility, and personal or business goals.
While both technologies offer immersive experiences, they serve different purposes and have unique advantages and limitations.
To make an informed decision, it’s crucial to understand the VR vs AR differences and evaluate which technology aligns best with your needs.

Understanding the Key Differences Between VR and AR
Before choosing between VR and AR, it’s essential to grasp their fundamental differences.
Virtual Reality (VR) – A Fully Immersive Digital World
- Complete Immersion: VR creates a fully digital environment, blocking out the real world to transport users into an entirely virtual space.
- Requires Special Equipment: VR headsets, such as Meta Quest, HTC Vive, and PlayStation VR, are necessary for experiencing virtual environments.
- Best for Gaming and Simulations: VR is widely used in gaming, training simulations, and virtual tourism, where users need a fully immersive experience.
- Limited Interaction with the Real World: Since VR replaces reality, users are fully disconnected from their physical surroundings.
Augmented Reality (AR) – Blending Digital Content with the Real World
- Enhances the Real World: Unlike VR, AR overlays digital elements onto the physical world rather than replacing it.
- Accessible Through Smartphones and Smart Glasses: AR experiences can be accessed using devices like smartphones, tablets, or AR smart glasses (e.g., Microsoft HoloLens, Magic Leap).
- Best for Retail, Navigation, and Education: AR is ideal for applications like virtual try-ons, interactive learning, and real-time navigation.
- Seamless Integration with Reality: Since AR blends digital elements with the physical environment, users can remain aware of their surroundings while engaging with the technology.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between VR and AR
1. Purpose and Use Cases
- Choose VR if: You need full immersion, such as for gaming, training simulations, remote collaboration in a virtual space, or VR-based therapy.
- Choose AR if: You want to enhance real-world experiences, such as for shopping (virtual try-ons), workplace productivity (remote assistance), or education (interactive learning).
2. Accessibility and Ease of Use
- VR requires specialized hardware and often dedicated space for movement-based experiences.
- AR is more accessible since most experiences can be accessed through smartphones and AR glasses, making it a more convenient option for everyday applications.
3. Cost and Budget Considerations
- VR headsets can be expensive, ranging from $300 to $1,500+, depending on the brand and specifications.
- AR is more cost-effective, as many AR experiences only require a smartphone, while advanced AR smart glasses (e.g., Microsoft HoloLens) may have higher price points.
4. User Experience and Comfort
- VR can cause motion sickness in some users due to the disconnect between visual movement and physical motion.
- AR is more comfortable since it does not remove users from their real-world surroundings.
5. Business and Industry Applications
- VR is ideal for:
- Gaming and entertainment
- Virtual training and education
- Healthcare (surgical training, therapy)
- Virtual tourism and real estate
- AR is best for:
- Retail (virtual try-ons, interactive shopping)
- Navigation and real-time information display
- Industrial use (remote assistance, manufacturing)
- Education (AR-based learning tools)
Making the Right Choice – Which One is Best for You?
If you’re still unsure whether to choose VR or AR, consider the following:
- For entertainment and deep immersion → Choose VR
- For practical, real-world applications → Choose AR
- For gaming, virtual meetings, or remote collaboration → VR is more suitable
- For enhancing business productivity, training, and real-time interaction → AR is the better option
Ultimately, both technologies have their own strengths, and in many cases, a combination of VR and AR may be the best approach for businesses and individuals looking to leverage immersive technology.
The Future of VR and AR
As technology advances, the line between VR and AR is blurring, leading to the rise of Mixed Reality (MR) and Extended Reality (XR).
These technologies combine elements of both VR and AR, allowing for even more immersive and interactive experiences.
The future of immersive tech is bright, with industries continuing to explore new ways to integrate VR and AR into our daily lives.
Whether you choose VR, AR, or a mix of both, one thing is certain—immersive technology is here to stay, and its impact will only grow.
👉 Ready to experience the future? Check out the best VR headsets here and explore top-rated AR smart glasses here to find the perfect fit for your needs!
Conclusion

Recap of the Differences and Similarities Between VR and AR
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are two pivotal technologies reshaping our interaction with digital content.
Understanding the “VR vs AR differences” is crucial for grasping their unique applications and potential.
Virtual Reality (VR):
- Immersion: VR offers a fully immersive experience by transporting users into a completely digital environment, effectively replacing the real world.
- Equipment: Users typically require specialized headsets, such as the Oculus Rift or HTC Vive, which block out physical surroundings to enhance immersion.
- Applications: VR is widely used in gaming, virtual tours, training simulations, and therapeutic settings, providing experiences that are entirely detached from the physical world.
Augmented Reality (AR):
- Overlay: AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception without replacing their environment.
- Accessibility: AR experiences can be accessed through smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses, making it more accessible to the general public.
- Applications: AR is prevalent in navigation systems, educational tools, retail (e.g., virtual try-ons), and interactive gaming, blending digital content with the physical world.
Similarities:
- Interactive Experiences: Both VR and AR provide interactive experiences that engage users in novel ways.
- Technological Foundation: They share underlying technologies, including sensors, cameras, and advanced computing, to create seamless experiences.
- Purpose: Both aim to enhance user engagement, whether by immersing them in a new environment (VR) or by enriching their current environment with additional information (AR).
The Evolving Landscape of Immersive Technologies and Their Potential Impact
The landscape of immersive technologies is rapidly evolving, with significant advancements in both VR and AR shaping various sectors.
Technological Advancements:
- Hardware Improvements: The development of lighter, more comfortable headsets and AR glasses is making prolonged use more feasible, enhancing user experience.
- Software Enhancements: Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) is leading to more responsive and personalized experiences in both VR and AR applications.
Market Growth:
- Expansion: The global market for immersive technologies is projected to reach $333 billion by 2025, indicating rapid adoption across industries.
- Consumer Adoption: Devices are becoming more affordable and user-friendly, leading to increased consumer interest and integration into daily life.
Integration Across Sectors:
- Education: Immersive technologies are revolutionizing learning by providing interactive and engaging educational tools.
- Healthcare: VR and AR are being utilized for surgical simulations, patient rehabilitation, and mental health treatments, improving patient outcomes.
- Entertainment: The entertainment industry is leveraging immersive technologies to create more engaging and interactive experiences for audiences.
Future Outlook:
As VR and AR technologies continue to evolve, their integration into various aspects of daily life is expected to deepen.
The convergence of VR and AR, often referred to as Mixed Reality (MR), is anticipated to offer even more seamless interactions between digital and physical worlds.
This evolution holds the potential to transform how we work, learn, and engage with our surroundings, making immersive technologies an integral part of our future.
Embrace the future of immersive experiences and stay ahead in the evolving digital landscape.
You might also like :

